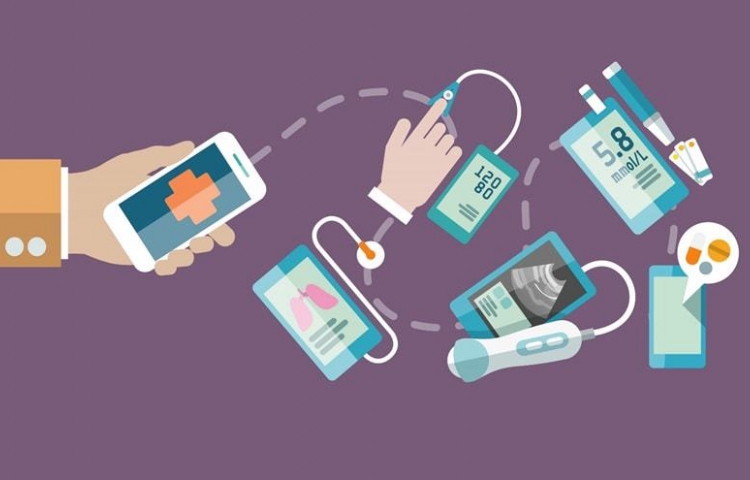

Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a technology to monitor patients outside of conventional clinical settings, such as in the home or in a remote area, which may increase access to care and decrease healthcare delivery costs. In hospitals, a lot of patients are admitted which makes it very difficult to monitor every patient simultaneously and this causes a lot of burden for doctors/nurses/staff. So, remote patient monitoring is a useful alternative to monitoring the patient. Incorporating RPM in chronic-disease management may significantly improve an individual’s quality of life, by allowing patients to maintain independence, prevent complications, and minimize personal costs. RPM facilitates these goals by delivering care through telecommunications. This form of patient monitoring can be particularly important when patients are managing complex self-care processes such as home hemodialysis. Key features of RPM, like remote monitoring and trend analysis of physiological parameters, enable early detection of deterioration; thereby reducing emergency department visits, hospitalizations, and the duration of hospital stays. While technologies are continually being developed to tackle this type of health care, physicians may utilize basic communication methods such as Zoom, Snapchat, or even landline phones.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, RPM has been used extensively and allowed for more fields such as psychology or cardiology to use virtual care. By 2025, the RPM industry is expected to double, due to factors such as the COVID-19 pandemic and increased at-home care.
Technological Components incorporated in RPM:
Most RPM technologies follow a general architecture that consists of four components:
- Sensors on a device that wireless communications enable to measure physiological parameters.
- Sensors can connect back to a central database by WiFi
- Local data storage at patients’ site that interfaces between sensors and other centralized data repositories and/or healthcare providers.
- Centralized repository to store data sent from sensors, local data storage, diagnostic applications, and/or healthcare providers.
- Diagnostic application software that develops treatment recommendations and intervention alerts based on the analysis of collected data.
Applications:
COVID-19: RPM can provide continuity of care for symptomatic COVID-19 patients post-discharge from the hospital and those with mild to moderate oxygen desaturation levels that do not require hospitalization and patients with long-COVID symptoms.
Cancer: The use of RPM among patients with cancer has been proven to improve outcomes overall, with studies showing improvements in rehospitalization rates and decreased healthcare resource usage. RPM has also been used with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), Dementia and falls, Diabetes, Congestive heart failure, Infertility, Telemedicine in prison systems, and many more diseases
Major Assignee for Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM):
1. MEDTRONIC: Medtronic is a major assignee, and it has 2514 filled patents. Medtronic is working on this technology since 1969.
2. PHILIPS: Philips is the second major assignee, and it has 2452 filled patents.
3. CARDIAC PACEMAKERS: Cardiac Pacemaker is the third major assignee, and it 1045 filled patents and
4. COVIDIEN: Covidien is the fourth major assignee, and it has more than 967 filled patents. Covidien is working on this technology since 1982.




Leave a comment: